Energy and Energy Conversion
Energy comes in many forms to perform a variety of tasks. Gasoline and diesel fuel give power to vehicles, tractors, and generators. Electricity powers lights, irrigation systems, pumps, and heating and cooling systems. Propane and natural gas can be used as fuel for hot water heaters or propane dryers. Many of these energy sources are nonrenewable, meaning they have limited availability and could run out before they could be replenished. Fossil fuels are the most common nonrenewable energy source. A fuel is a substance that stores energy. Renewable energy sources are defined as those that can be replenished or replace themselves through natural reproduction or other processes. Biomass is an example of a renewable resource. Inexhaustible energy resources include solar, wind, water (hydro), and geothermal.
To make energy useful, it is converted from its original source and then transferred from one place to another. For example, solar panels collect energy from the sun and then transfer it from light energy to heat and electrical energy. Biomass is organic material that comes from plants and animals. Through photosynthesis, plants take and store energy from the sun. The resulting organic material is then burned directly or converted to a liquid biofuel or biogas that can be burned as a fuel. Consider the following examples:
- Wood is burned to heat buildings and can be used to generate electricity.
- Agricultural crops and waste materials can be burned as a fuel or converted to liquid biofuels.
- Food waste can be burned to generate electricity in power plants.
- Animal waste (manure) and human sewage can be converted to biogas and burned as a fuel.
Animal Agriculture and Manure Management
Animal agriculture produces protein-rich food to eat such as meat, milk, and eggs. These products come from farms of all sizes and types and are produced by animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs, chickens, and turkeys. Animal agriculture also produces many byproducts. A byproduct is an incidental or secondary product made in the manufacture or synthesis of something else. For example, pork meat is the primary product produced on a hog farm. However, other products such as pharmaceuticals (medications), leather, paint brush bristles, pet food, cosmetics, and more also come from pigs as byproducts. Organic by-products or "wastes" of the livestock industry include solid and liquid manures, used bedding, and spilled feed.4 However, manure accounts for the majority of animal waste products.
The proper management of manure is the responsibility of all animal farms regardless of the livestock they raise or the size of their operation. In reference to manure management, best management practices can help protect the environment, improve the health and well-being of livestock animals, and aid in the useful cycling of soil nutrients. Manure contains macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium as well as micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. The nutrient value of manure depends on the animal species, feed ration, and the method of manure collection, but manure is part of many nutrient recycling programs.5
Manure management strategies on the farm vary by animal species and the type of housing the animals live in. Management strategies include plans for how manure is captured, stored, treated, and used.6 While manure can be a useful byproduct from an animal farm, its management also presents some challenges. For example, if not managed properly, manure can affect water quality. The over-application of manure nutrients to cropland can increase the risk of contaminating surface water. Manure contributes to greenhouse gas emissions representing 10% of GHG emissions from global livestock production.7 A final challenge to mention in the managment of manure is the odor that could impact residential areas located near animal farms. Odor intensity has many contributing factors including the farm's location, animal species, type of animal housing, and weather (especially moisture and wind). Technologies and research helps to improve strategies used by farmers to efficiently manage their manure waste.
Technological Solutions to Decrease Environmental Impact
Technological advancements in agriculture over previous decades have made it possible for farmers to feed a growing population by increasing both production and efficiency on the farm. Improved knowledge of science and genetics has helped farmers selectively breed livestock animals to be more efficient. Coupled with better animal nutrition, modern livestock farms yield high quantities of meat, milk, and eggs. Farms can be relatively small or large in size. Regardless of size or production style, animals produce waste that must be managed. Technology is finding solutions for effective uses for animal waste that decrease the environmental footprint of agriculture.
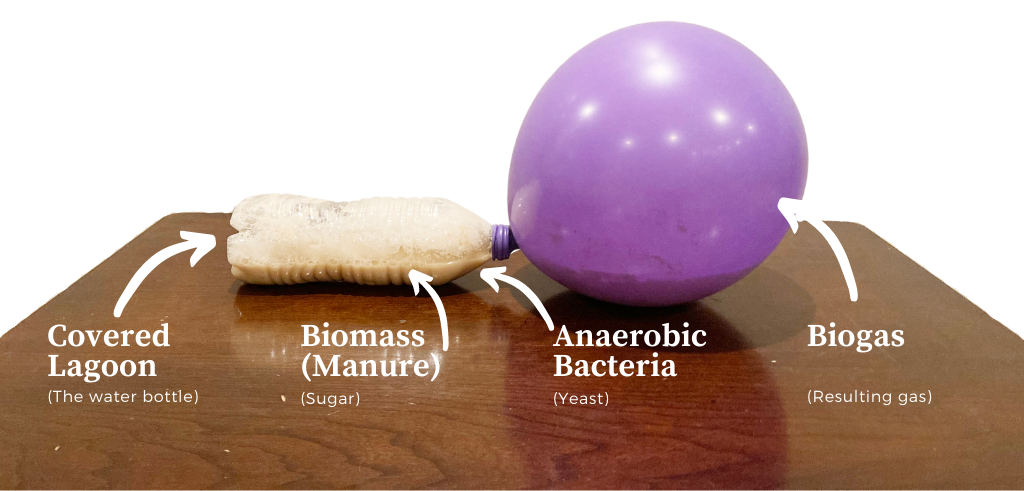
The science of anaerobic digestion captures energy from animal waste (manure). Basically, manure and other organic waste is loaded into an airtight tank where special anaerobic bacteria (that live without oxygen) consume the waste and give off methane. Methane is a very flammable gas (like propane) that can power generators efficiently. The process has benefits that include:
- Disposing of waste that can have harmful effects to water quality when not managed correctly. Treated manure can also be recycled on farmland as nutrient-rich, organic fertilizer for cropland in adherence with regulatory requirements.
- Preventing methane from entering the atmosphere. Methane is a greenhouse gas that is about 23 times more powerful than carbon dioxide in trapping heat in the atmosphere. By trapping and burning it up in generators, GHG impacts are avoided.
- Allowing farmers to generate electricity and heat from their own animal waste. Farmers who invest in digesters will see a return on their investment via free electricity and heat, often within ten years. This financial incentive is especially attractive given the rising cost of fuel.
- Controlling the smell from livestock operations. Digesters can also help farmers control the smell of livestock operations.