Many foods we eat are plants. Plant-based foods provide essential nutrients including many vitamins and minerals. These plant foods can be an excellent teaching tool for understanding the external parts of a plant – roots, stems, leaves, fruits, and flowers. Farmers grow and harvest many plant-based foods such as carrots, green beans, kale, sweet potatoes, and strawberries which are part of a healthy diet.
Each of these food items are grown from a plant either above or below the surface of the soil. For this lesson student's experience for eating fruits and vegetables that live and grow above ground or underground would be required for helping them gain an understanding for identifying where they belong on the USDA's MyPlate diagram. Teachers should be familiar with the MyPlate graphic organizer, including food categories. If not, please review the information at www.myplate.gov.
Roots are usually found underground with the functions of anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. In some plants they also serve as a storage area for food for the plant. For some plants, such as rutabagas, radishes, carrots, and sugar beets, the root is the crop.
Stems are the main stalk of a plant. Usually stems grow above ground and transport water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and flower. The leaves produce food (glucose) which is also transported throughout the plant by the stem. You can think of the stem as a passage way for water and food. In addition, the stem serves as a backbone, offering the plant support and structure. Edible stems that grow above ground include asparagus, broccoli, and cauliflower.
The leaves of a plant serve as solar panels. They collect sunlight and use this solar energy to power photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs in the leaf. The plant takes in water and carbon dioxide. The sun’s energy causes a chemical reaction which converts the water and carbon dioxide into glucose (food for the plant) and oxygen. The plant uses the glucose to grow and the oxygen is given off into the environment. Humans eat several plant-based foods with edible leaves such as cabbage, kale, lettuce, and spinach.
The flower of a plant is designed for reproduction. The petals, or modified leaves, attract pollinators that transfer pollen so seeds can be produced in the flower. Broccoli and cauliflower flowers can be eaten known as the flowerets.
The fruit is the ripened ovary of the flower of a plant. Seeds are contained inside of the fruit. Many seeds can be eaten or also used to grow new plants. Humans enjoy eating the following fruits such as apples, strawberries, watermelons, and grapes, just to name a few.
Vegetables and fruits make up two of the five categories found on the USDA's MyPlate diagram. Each section is color coded and properly sized to help consumers quickly identify where each food item is categorized onto a place setting. The vegetable section is green and is slightly larger than the red colored fruit section. The MyPlate graphic organizer can be found on the website www.myplate.gov that was developed and maintained by USDA Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion. In addition to vegetables and fruits, the MyPlate image also includes dairy, grains, and protein. Before sitting down to a meal at home or school, the MyPlate campaign can aid students in making better decisions about the foods they choose to eat.
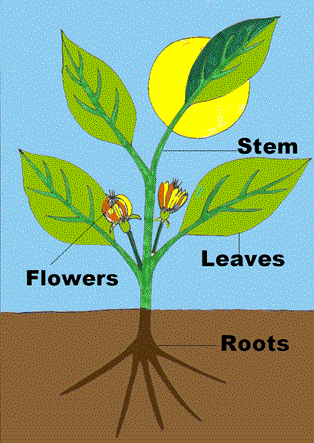 Inform students that vegetables and fruits are plants. Draw or show a picture of the common parts of a plant
Inform students that vegetables and fruits are plants. Draw or show a picture of the common parts of a plant
 Show students the book Tops and Bottoms by Janet Stevens. Tell students that this book is about a rabbit and a bear who decided to grow some plants to eat. The title is Tops and Bottoms. Ask the students:
Show students the book Tops and Bottoms by Janet Stevens. Tell students that this book is about a rabbit and a bear who decided to grow some plants to eat. The title is Tops and Bottoms. Ask the students: